Sports knee injury refers to any injury affecting the knee joint that occurs during sport, exercise, or any athletic activities. The cartilage of the knee can be acutely injured or can gradually tear by overuse, sudden twists or impacts, or improper technique. These injuries can range from mild strains or sprains to more severe ligament tears, cartilage damage, or tendon injuries.

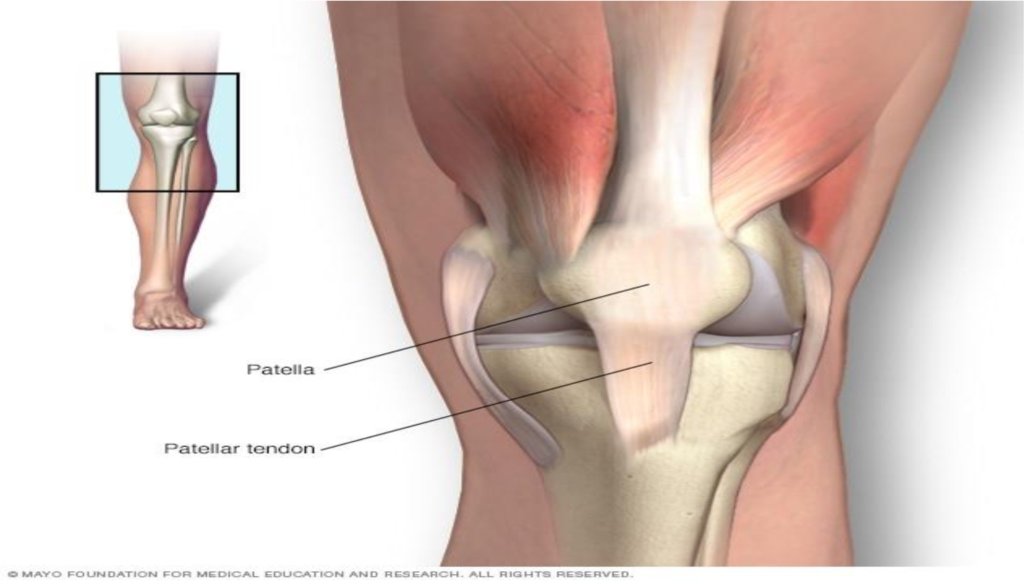
Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is a common overuse of injury characterized by inflammation or degeneration of patellar tendon, which connect the kneecap[patella] to the shinbone[tibia].
Causes for Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendinitis is a common overuse injury, caused by repeated stress on your patellar tendon. The stress results in tiny tears in the tendon, which your body attempts to repair.
But as the tears in the tendon multiply, they cause pain from inflammation and weakening of the tendon. When this tendon damage persists for more than a few weeks, it’s called tendinopathy.
Subluxation is another word for partial dislocation of a bone. Patellar subluxation is a partial dislocation of the kneecap (patella). It’s also known as patellar instability or kneecap instability.The kneecap is a small protective bone that attaches near the bottom of your thigh bone (femur). As you bend and straighten your knee, your
kneecap moves up and down in a groove at the bottom of the thigh, called the trochlea.
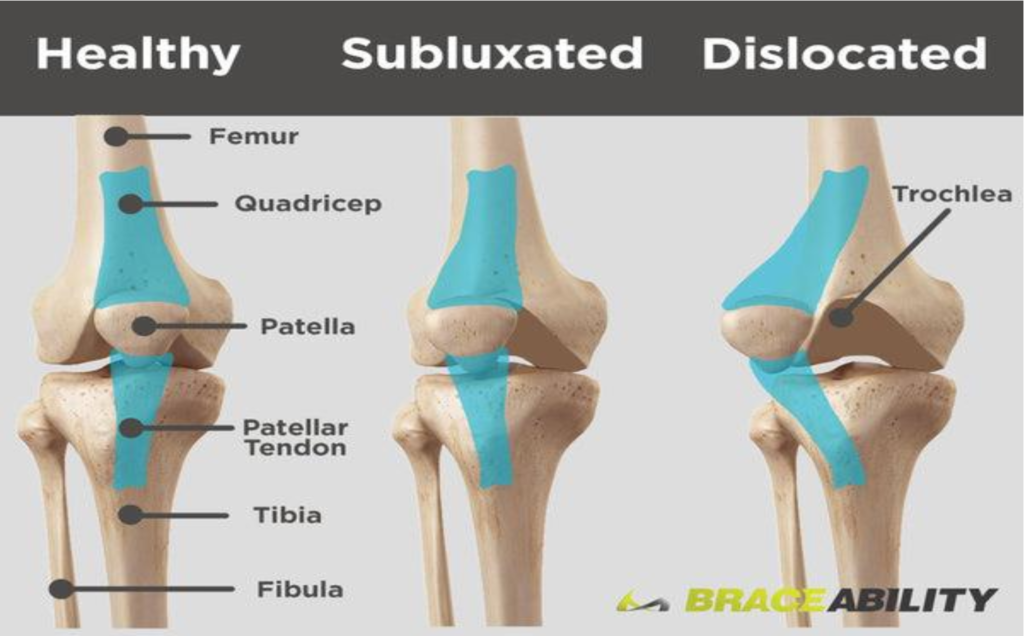
Causes of Subluxtion of patella
Symptoms of Patellar Subluxation May Include:
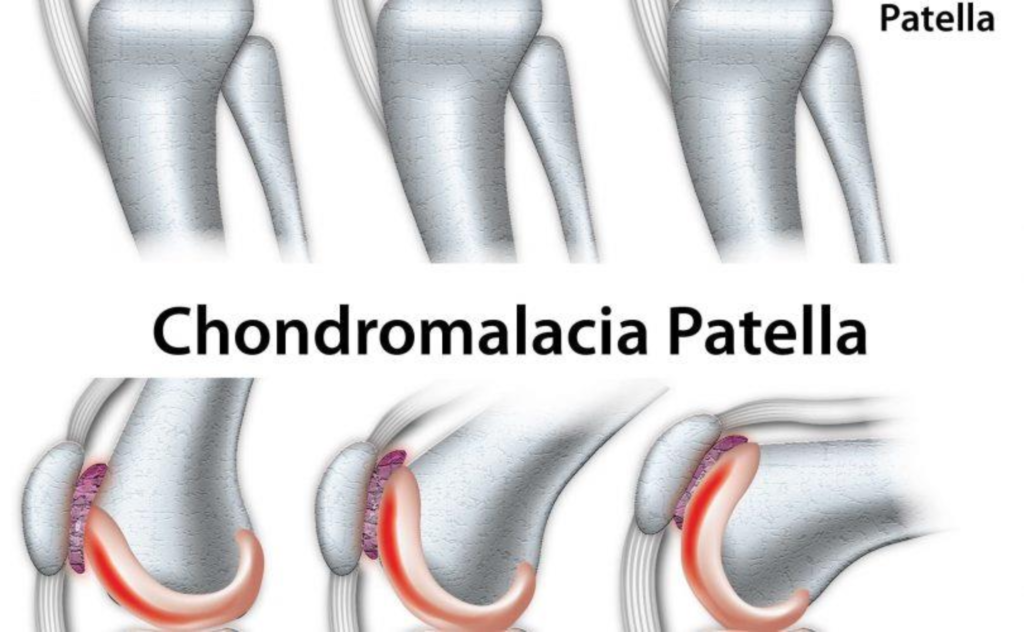
Chondromalacia patella (or patellae), also referred to as “runner’s knee” is a condition in which the cartilage cushioning the area under the patella (kneecap) begins to deteriorate and wear out. Due to this, the kneecap may start to rub against the femur (thigh bone) and cause discomfort or pain.
Causes of Chondromalacia Patellae
Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) is a growth-related, overuse injury most commonly seen in young adolescents. This disease is characterized by a painful inflammation (bump) located at your child’s tibial tuberosity. Your child’s tibial tuberosity is located about an inch below their kneecap (patella) at the growth plate where their patellar tendon attaches to their shinbone (tibia). OSD typically occurs during periods of rapid growth, when bones, muscles, and tendons are developing.
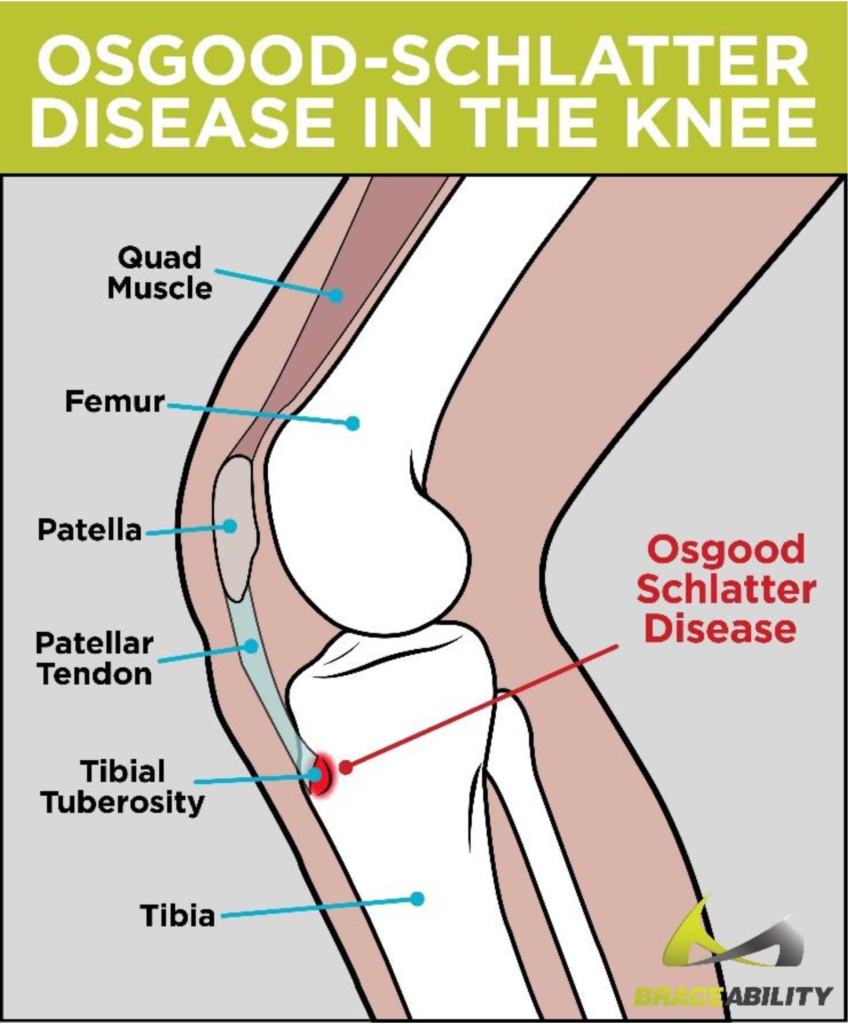
Signs and symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter
disease include:
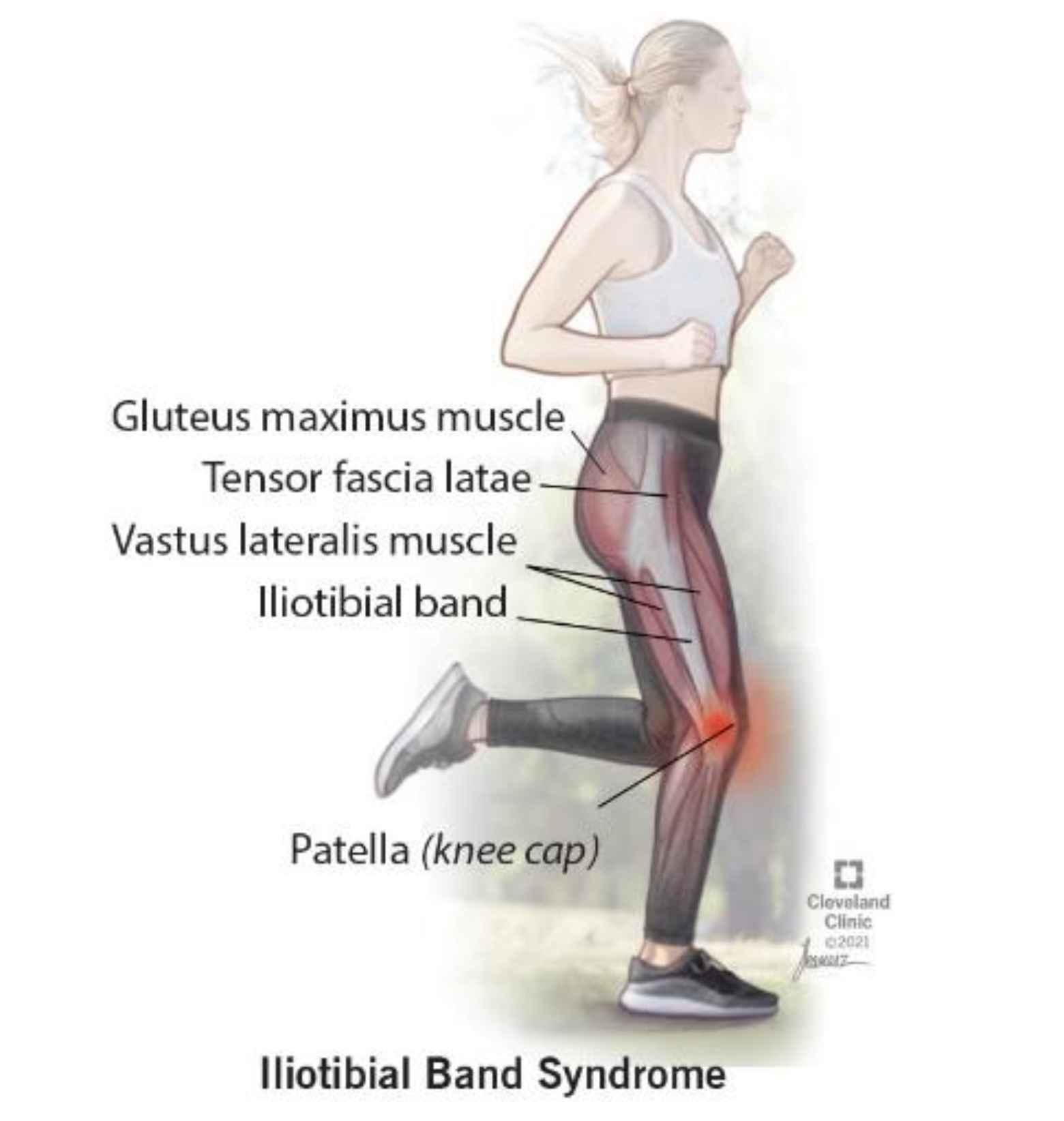
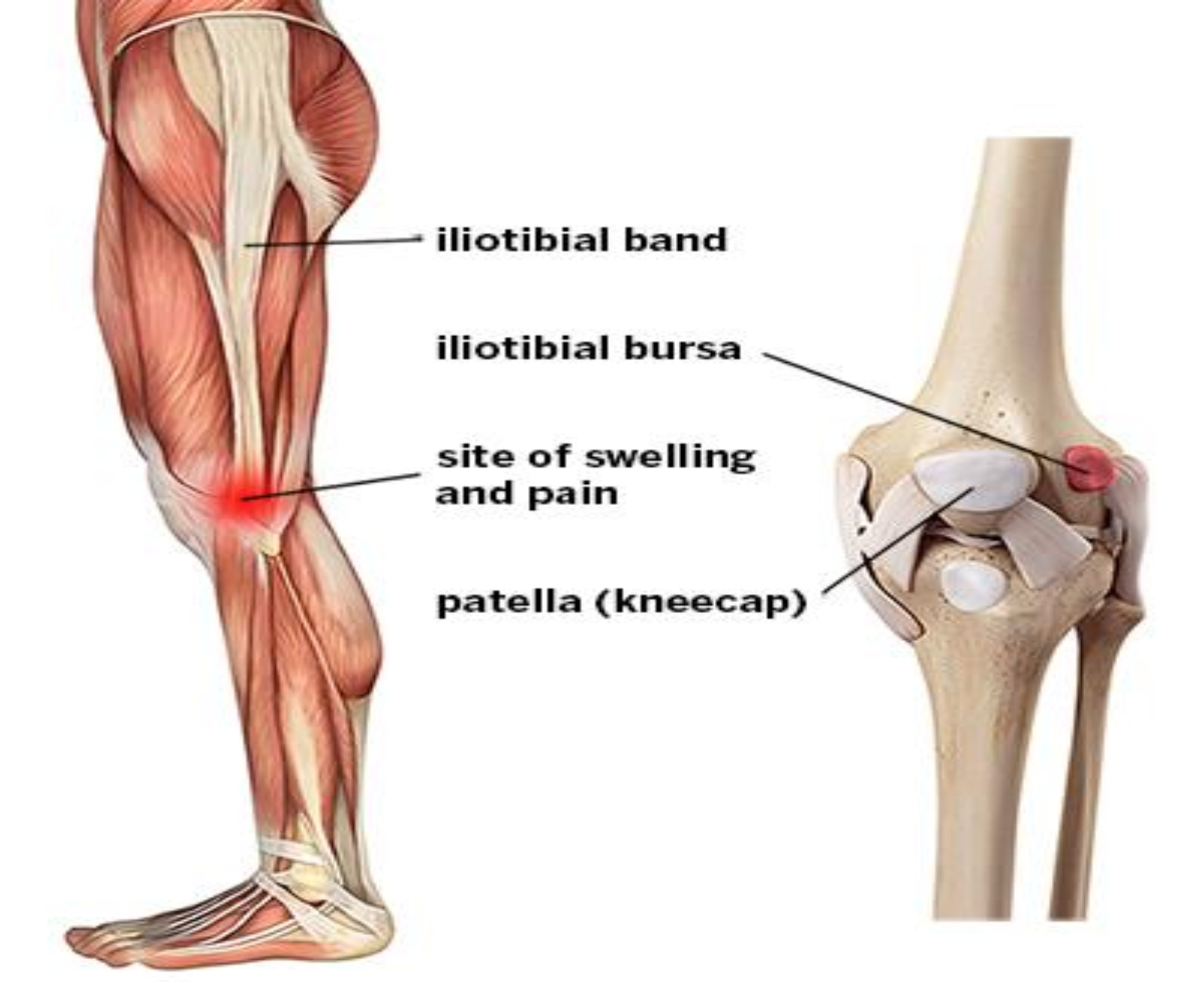
Causes of IT band syndrome.
ITBS is caused by excessive friction from the IT band being overly tight and rubbing against bone. It’s primarily an overuse injury from repetitive movements. ITBS causes friction, irritation, and pain when moving the knee. It seems to happen only in some people, though the reasons for this are unclear.
It’s especially common for cyclists and runners. It can even develop from repetitively walking up and down stairs, wearing high heels, or sitting for long periods with bent knees.
Symptoms of IT band syndrome may include:
How is iliotibial band syndrome treated?
Most cases of iliotibial band syndrome heal on their own without
surgery. An athlete may need to take time off from sports to give
their leg time to recover. The amount of time depends in part on the
extent of the injury.
Treatment may include:
Please complete the form below to request an appointment. A member of our intake team will follow up with you.
Vraj Complex, 302, 100 Feet Rd, Near Shyamal Cross road, Jodhpur Village, Ahmedabad, Gujarat 380015